What is Mobile App Development?
Mobile app development refers to the process of creating software applications designed to run on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. These applications can be pre-installed or downloaded and installed by users from app stores or other online sources.
There are three main types of mobile apps:
- Native Apps: Native apps are developed specifically for a particular mobile operating system (OS), such as iOS for Apple devices or Android for devices running on the Android platform. They are built using the programming languages and development tools supported by the respective OS, ensuring optimal performance and seamless integration with the device’s hardware and software features.
- Hybrid Apps: Hybrid apps are a combination of native and web-based technologies. They are typically built using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, wrapped in a native container that allows them to access device features and be distributed through app stores. This approach provides a balance between cross-platform compatibility and native-like performance.
- Web Apps: Web apps are essentially websites optimized for mobile devices. They are built using standard web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, and can be accessed through a mobile web browser without the need for installation. Web apps are platform-independent and can run on any device with a compatible web browser.
In today’s digital age, mobile apps have become an integral part of our daily lives. They offer convenience, entertainment, productivity tools, and access to a wide range of services and information. Mobile apps have revolutionized industries such as e-commerce, banking, social media, gaming, and more, providing users with a seamless and personalized experience on the go.
The importance of mobile app development lies in its ability to reach a vast global audience and cater to the increasing demand for mobile-friendly solutions. With the widespread adoption of smartphones and tablets, businesses and developers alike recognize the need to create engaging and user-friendly mobile apps to stay competitive and meet the ever-evolving needs of consumers.
Skills Needed for Mobile App Development
To become a successful mobile app developer, you need to possess a diverse set of skills. Here are some essential skills required for mobile app development:
Programming Languages: Proficiency in programming languages like Java (for Android app development), Swift or Objective-C (for iOS app development), and Kotlin (for Android app development) is crucial. These languages are the foundation for building mobile applications on their respective platforms.
User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) Design: Mobile app developers must have a good understanding of UI/UX design principles to create visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces. Knowledge of design tools like Adobe XD, Sketch, or Figma is beneficial for creating wireframes, mockups, and prototypes.
Database Management: Most mobile apps require data storage and retrieval, making database management skills essential. Familiarity with SQL and NoSQL databases, such as SQLite, Realm, Firebase Realtime Database, and Core Data, is valuable.
APIs and Web Services: Mobile apps often interact with servers and external services through APIs. Understanding how to consume and integrate APIs, as well as knowledge of RESTful web services and JSON data formats, is important.
Version Control: Familiarity with version control systems like Git is necessary for collaborating with other developers, tracking changes, and managing code repositories.
Testing and Debugging: Mobile app developers should be skilled in testing techniques, such as unit testing, integration testing, and UI testing. Proficiency in debugging tools and techniques is also essential for identifying and resolving issues.
Mobile Platform Specifics: Developers need to understand the specific guidelines, design patterns, and best practices for the mobile platforms they are targeting, such as Android and iOS.
Continuous Integration and Deployment: Knowledge of continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) practices and tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, or CircleCI is beneficial for streamlining the development and release process.
Agile Methodologies: Familiarity with agile development methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, is valuable for collaborating with cross-functional teams and delivering high-quality mobile apps efficiently.
While this list covers many essential skills, mobile app development is a constantly evolving field, and developers should be prepared to continuously learn and adapt to new technologies and trends.
Mobile App Development Frameworks and Tools
Mobile app development involves working with various frameworks, languages, and tools, depending on the target platform (iOS or Android) and the development approach (native or cross-platform). Here are some popular frameworks and tools used in mobile app development:
React Native: React Native is a cross-platform framework developed by Facebook that allows developers to build native mobile apps using JavaScript and React. It provides a way to create a single codebase that can run on both iOS and Android platforms, reducing development time and effort.
Flutter: Flutter is an open-source UI software development kit created by Google. It uses the Dart programming language and allows developers to build high-performance, visually attractive, and natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase.
Xamarin: Xamarin is a Microsoft-owned cross-platform framework that allows developers to build native mobile apps for iOS, Android, and Windows using C# and .NET. It provides a shared codebase and native user interface controls, resulting in a native app experience.
Android Studio: Android Studio is the official Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for Android app development. It is based on IntelliJ IDEA and provides tools for building, testing, and debugging Android applications.
Xcode: Xcode is Apple’s IDE for developing software for macOS, iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, and tvOS. It includes a suite of tools for designing user interfaces, writing code, testing, and submitting apps to the App Store.
Native Development Tools: For building native mobile apps, developers use platform-specific languages and tools. For iOS development, Swift and Objective-C are the primary languages, along with Xcode as the IDE. For Android development, Java and Kotlin are the main languages, with Android Studio as the IDE.
These frameworks and tools offer different features, performance characteristics, and learning curves. Developers often choose a framework or tool based on their existing skillset, project requirements, target audience, and development team preferences.
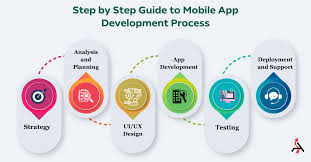
Mobile App Development Process
The mobile app development process typically follows a structured approach to ensure a high-quality and successful app. Here are the common stages involved:
- Ideation and Planning: This initial stage involves brainstorming app ideas, defining the app’s purpose, target audience, and unique value proposition. Conducting market research and analyzing competitor apps is crucial to validate the idea and identify potential gaps or opportunities.
- Requirements Gathering and Analysis: Once the idea is solidified, the next step is to gather and document detailed requirements for the app. This includes functional requirements (features and functionalities), non-functional requirements (performance, security, usability), and any specific platform or device constraints.
- Wireframing and Prototyping: Wireframes and prototypes are created to visualize the app’s user interface (UI) and user experience (UX). Wireframes are low-fidelity sketches that outline the app’s structure and layout, while prototypes are interactive models that simulate the app’s functionality and navigation.
- Design and UI/UX Development: Based on the wireframes and prototypes, the app’s visual design and user interface are developed. This stage involves creating high-fidelity mockups, selecting color schemes, typography, icons, and other visual elements. Emphasis is placed on creating an intuitive and engaging user experience.
- App Development (Coding): The actual coding and development of the app take place during this stage. Developers write code using the chosen programming languages and frameworks, integrating various features, APIs, and libraries as needed. Version control systems like Git are commonly used to manage the codebase.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing is essential to identify and fix bugs, ensure compatibility across different devices and platforms, and validate the app’s functionality. This stage includes unit testing, integration testing, performance testing, usability testing, and security testing.
- Deployment and Release: Once the app has been thoroughly tested and approved, it is ready for deployment. This involves submitting the app to the respective app stores (e.g., Apple App Store, Google Play Store) and following their guidelines for app submission and review. App metadata, such as descriptions, screenshots, and keywords, is also prepared for the app store listing.
- Maintenance and Updates: After the app is released, the development process continues with ongoing maintenance, bug fixes, and updates. User feedback is monitored, and new features or improvements are planned and implemented in subsequent app updates or new versions.
Throughout the development process, collaboration between cross-functional teams (developers, designers, project managers, and stakeholders) and effective communication are crucial for successful app delivery. Agile methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, are often employed to enable iterative development, adaptability, and continuous improvement.
Designing User-Friendly Mobile Apps
Creating a user-friendly mobile app is paramount to its success. A well-designed app using app maker platform should prioritize user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) principles, ensuring seamless navigation, intuitive interactions, and a visually appealing interface. Here are some best practices to consider:
User-Centric Design: Understand your target audience’s needs, preferences, and behaviors. Conduct user research, create personas, and design with your users in mind. Empathize with their goals and pain points to create solutions that resonate with them.
Simplicity and Clarity: Mobile apps should be easy to understand and use. Avoid cluttered layouts, complex navigation, and unnecessary features. Prioritize essential functionalities and present information in a clear, concise manner.
Consistent UI Design: Maintain consistency in visual elements, such as typography, color schemes, icons, and layout patterns. Consistent design enhances familiarity and reduces cognitive load, making the app more intuitive to use.
Intuitive Navigation: Design a logical and intuitive navigation system that aligns with common mobile patterns and gestures. Use clear labels, icons, and visual cues to guide users through the app’s flow.
Responsive and Adaptive Design: Ensure your app adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes, resolutions, and orientations. Utilize responsive design techniques to provide an optimal viewing and interaction experience across various devices.
Accessibility: Consider users with disabilities by incorporating accessibility features, such as alternative text for images, proper color contrast ratios, and support for screen readers and voice control.
Performance Optimization: Optimize your app’s performance by minimizing load times, ensuring smooth transitions and animations, and efficiently managing resources to prevent lags or freezes.
Feedback and Error Handling: Provide clear feedback and error messages to users when something goes wrong or an action is successful. Offer helpful guidance and solutions to resolve issues.
Iterative Testing and Refinement: Continuously test your app with real users, gather feedback, and refine the design based on their insights. Iterate and improve the user experience through multiple cycles of testing and refinement.
Remember, designing a user-friendly mobile app is an ongoing process that requires a deep understanding of your users, attention to detail, and a commitment to continuously improving the user experience.
Testing and Debugging Mobile Apps
Testing and debugging are critical stages in the mobile app development lifecycle. They help ensure that your app functions correctly, provides a seamless user experience, and meets all the necessary requirements. Thorough testing and debugging can identify and resolve issues before the app is released, saving you from potential negative reviews, user frustration, and costly fixes down the line.
Mobile app testing typically involves various methods, including:
- Unit Testing: This involves testing individual components or modules of the app to verify their functionality and behavior.
- Integration Testing: This tests how different components of the app work together and interact with each other.
- Usability Testing: This evaluates the app’s user interface, navigation, and overall user experience to ensure it’s intuitive and user-friendly.
- Performance Testing: This assesses how the app performs under different conditions, such as varying network speeds, device configurations, and load scenarios.
- Security Testing: This checks for potential vulnerabilities and ensures that the app follows best practices for data protection and user privacy.
- Compatibility Testing: This verifies that the app runs smoothly across different devices, operating systems, and screen sizes.
Several tools and frameworks are available to facilitate mobile app testing and debugging. Some popular options include:
- Automated Testing Frameworks: Tools like Appium, Espresso (for Android), and XCUITest (for iOS) enable automated testing of mobile apps.
- Debugging Tools: Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) like Android Studio and Xcode provide built-in debugging tools for inspecting app behavior, setting breakpoints, and tracking variables.
- Device Emulators and Simulators: These tools allow you to test your app on various virtual devices without the need for physical hardware.
- Performance Monitoring Tools: Tools like New Relic, Crashlytics, and Firebase Performance Monitoring help track app performance, identify bottlenecks, and monitor crash reports.
Effective testing and debugging practices not only improve the quality of your mobile app but also contribute to better user satisfaction and retention. By identifying and resolving issues early in the development cycle, you can deliver a polished and reliable product to your users.
App Store Submission and Marketing
Submitting your app to the major app stores, such as the Google Play Store and Apple App Store, is a crucial step in the mobile app development process. Each platform has specific guidelines and requirements that you must follow for your app to be approved and listed.
For the Google Play Store, you’ll need to create a developer account, provide detailed information about your app, including screenshots, descriptions, and pricing details. You’ll also need to digitally sign your app with a private key and follow Google’s content policies and technical guidelines.
The process for submitting to the Apple App Store is similar, but with its own set of requirements. You’ll need to enroll in the Apple Developer Program, create a code-signing certificate, and submit your app through App Store Connect. Apple has stringent guidelines for app design, functionality, and content, so it’s essential to review and adhere to their guidelines carefully.
Once your app is approved and listed on the app stores, App Store Optimization (ASO) becomes crucial for increasing visibility and downloads. ASO involves optimizing your app’s title, description, keywords, and visuals to rank higher in app store search results and browse sections.
Effective ASO strategies include conducting keyword research, crafting compelling app descriptions, utilizing high-quality visuals (screenshots and app previews), and encouraging positive reviews and ratings from users. Additionally, you can leverage app store features like in-app purchases, subscriptions, and app bundles to drive revenue and engagement.
Marketing your app is equally important for its success. You can leverage various marketing channels, such as social media, influencer collaborations, content marketing, and paid advertising campaigns. Building a strong brand identity, creating engaging content, and leveraging user communities can also help promote your app and foster a loyal user base.
Remember, app store submission and marketing are ongoing processes. Regularly updating your app with new features, bug fixes, and optimizations can help maintain its visibility and relevance in the app stores. Continuously monitoring user feedback, analytics, and market trends can inform your marketing strategies and ensure your app remains competitive in the ever-evolving mobile app landscape.
Monetization Strategies for Mobile Apps
Mobile app monetization strategies play a crucial role in generating revenue and ensuring the long-term sustainability of your app business. With a vast array of monetization models available, it’s essential to choose the right approach that aligns with your app’s purpose, target audience, and overall business goals. Here are some popular monetization strategies to consider:
In-App Purchases (IAPs): This model allows users to download your app for free, but they must pay for additional features, content, or virtual goods within the app. IAPs can take the form of consumable items (e.g., virtual currency, power-ups) or non-consumable items (e.g., premium features, ad removal). IAPs are particularly effective for gaming apps, productivity tools, and content-based apps.
Advertising: By incorporating advertisements into your app, you can generate revenue from impressions, clicks, or conversions. This model works well for apps with a large user base and high engagement rates. However, it’s crucial to strike a balance between ad placement and user experience to avoid disrupting the app’s functionality.
Subscriptions: This monetization strategy involves charging users a recurring fee (monthly, yearly, or one-time) to access premium features or content within your app. Subscriptions are suitable for apps that offer continuous value, such as streaming services, productivity tools, or premium content libraries.
Freemium Model: This approach combines a free version of your app with a premium version that offers additional features or functionality. Users can try the free version and upgrade to the premium version if they find value in the app. This model can be effective for attracting a large user base and converting a portion of users to paid subscribers.
Sponsorships and Partnerships: You can explore partnerships with brands or businesses that align with your app’s target audience. These partnerships can involve sponsored content, product placements, or co-branded offerings, generating revenue through sponsorship fees or revenue sharing agreements.
Paid Apps: While less common in today’s app market, you can opt for a traditional paid app model, where users must purchase your app upfront to access its features and content. This approach can work well for niche or highly specialized apps that offer significant value to users.
It’s important to note that different monetization strategies may work better for different app categories and target audiences. Additionally, you can combine multiple monetization models to diversify your revenue streams and cater to varying user preferences. Continuously analyzing user behavior, engagement metrics, and market trends can help you refine your monetization strategy and maximize revenue potential.
Mobile App Security and Privacy
Mobile app security and user privacy are critical considerations in today’s digital landscape. As mobile devices become increasingly integrated into our daily lives, ensuring the safety of user data and protecting against potential threats is paramount. Developers must prioritize security measures from the initial design phase to safeguard sensitive information and maintain user trust.
One of the primary concerns in mobile app security is data protection. Apps often handle sensitive user data, such as personal information, financial details, and location data. Implementing robust encryption techniques and secure data storage practices is essential to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches. Additionally, adhering to industry-standard security protocols, such as SSL/TLS for secure communication, is crucial.
Another key aspect of mobile app security is input validation and sanitization. Malicious actors may attempt to inject malicious code or exploit vulnerabilities through user input fields. Developers should implement stringent input validation mechanisms to prevent code injection attacks, such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
User authentication and authorization also play a vital role in mobile app security. Implementing strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, and secure session management can help protect against unauthorized access and account hijacking attempts. Additionally, regular security audits and penetration testing can identify potential vulnerabilities and mitigate risks.
Regarding user privacy, mobile apps should prioritize transparency and provide clear privacy policies outlining how user data is collected, used, and shared. Adhering to data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), is crucial for maintaining compliance and building user trust.
Best practices for secure coding include following the principle of least privilege, where apps only request and access the minimum necessary permissions and data. Implementing secure coding practices, such as input validation, output encoding, and secure coding patterns, can help prevent common vulnerabilities and reduce the attack surface.
Regular security updates and patches are also essential for maintaining app security. Developers should stay informed about the latest security threats and vulnerabilities and promptly address them through updates and patches.
By prioritizing mobile app security and user privacy from the outset, developers can build trustworthy and secure applications that protect user data and maintain a positive reputation in the market.
Continuous Learning and Staying Up-to-Date
The world of mobile app development is constantly evolving, with new technologies, frameworks, and best practices emerging regularly. To remain competitive and relevant in this field, it is crucial for developers to embrace a mindset of continuous learning and stay updated with the latest trends.
Mobile operating systems like iOS and Android receive frequent updates, introducing new features, APIs, and design guidelines. Developers must stay informed about these changes and adapt their skills accordingly to ensure their apps remain compatible and take advantage of the latest functionalities.
Additionally, new programming languages, frameworks, and tools are continuously being developed to streamline the app development process and enhance app performance. Keeping up with these advancements can help developers write more efficient, maintainable, and scalable code.
Attending industry conferences, workshops, and meetups can be an excellent way to learn from experienced professionals, network with peers, and gain insights into emerging technologies and best practices. Online resources, such as blogs, forums, and online courses, can also provide valuable learning opportunities.
Furthermore, participating in open-source projects or contributing to developer communities can help developers stay engaged with the latest trends, learn from experienced developers, and contribute their own knowledge and expertise.
By embracing continuous learning and staying up-to-date with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices, mobile app developers can future-proof their skills, deliver high-quality apps, and remain competitive in the ever-evolving mobile app development landscape.
Mobile App Development Career Paths
Mobile app development offers a variety of career paths and opportunities. One option is to work as a freelance developer, taking on projects for clients and building apps on a contract basis. This allows for flexibility and the ability to work on diverse projects, but requires strong self-discipline and business skills.
Another path is to join a company or organization as an in-house mobile app developer. This provides a stable income, benefits, and the opportunity to work as part of a team. Companies of all sizes, from startups to large enterprises, hire mobile app developers to build and maintain their apps.
For those with an entrepreneurial spirit, starting your own app business can be a rewarding path. This involves identifying a market need, developing an app to meet that need, and then marketing and monetizing the app. It’s a higher-risk, higher-reward approach that requires a combination of technical skills, business acumen, and perseverance.
Within these broad categories, there are also specializations based on platforms (iOS, Android, cross-platform), industries (gaming, finance, healthcare, etc.), and roles (front-end, back-end, full-stack, UI/UX design, etc.). As the mobile app industry continues to grow and evolve, new career opportunities and niches are likely to emerge.
Regardless of the path chosen, continuous learning and staying up-to-date with the latest technologies, trends, and best practices is essential for success in mobile app development. Building a strong portfolio, networking, and gaining practical experience through internships or personal projects can also help pave the way for a rewarding career in this dynamic field.
Getting Started with Mobile App Development
If you’re new to mobile app development, the journey might seem daunting at first. However, with the right resources and a structured approach, you can kickstart your learning process and build your skills step-by-step. Here are some tips and resources to help you get started:
- Online Courses: Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and edX offer a wide range of online courses covering various aspects of mobile app development. These courses provide structured learning paths, hands-on projects, and often include certificates upon completion.
- Tutorials and Documentation: Official documentation and tutorials from platform providers like Apple (for iOS) and Google (for Android) are invaluable resources. These resources provide in-depth explanations, code samples, and best practices directly from the source.
- Coding Challenges and Practice Projects: Hands-on practice is crucial for reinforcing your learning. Participate in coding challenges, build small practice apps, or contribute to open-source projects to apply your knowledge and gain real-world experience.
- Community Forums: Join online communities and forums dedicated to mobile app development, such as Stack Overflow, Reddit’s r/androiddev or r/iOSProgramming, and platform-specific forums. These communities offer a wealth of knowledge, allowing you to ask questions, seek advice, and learn from experienced developers.
- Local Meetups and Events: Attend local meetups, hackathons, or developer conferences to connect with other developers, learn from experts, and stay updated on the latest trends and best practices in the industry.
- Mentorship and Collaboration: Consider finding a mentor or joining a study group to collaborate with others on projects. Mentors can provide guidance and feedback, while collaboration fosters knowledge sharing and teamwork skills.
- Version Control and Project Management: Familiarize yourself with version control systems like Git and project management tools like Jira or Trello. These tools are essential for working on real-world projects, collaborating with teams, and managing code changes.
- Continuous Learning: Mobile app development is a rapidly evolving field, so make continuous learning a habit. Stay up-to-date with the latest platform updates, new tools, and emerging technologies by following industry blogs, subscribing to newsletters, and attending online or in-person events.
Remember, learning mobile app development is a journey, and consistency and perseverance are key. Start small, build projects, and gradually expand your skills and knowledge. With dedication and the right resources, you can become a proficient mobile app developer.